Configure a user in AWS IAM that is required to use MFA to connect to S3
You want an IAM user who cannot directly access S3, but instead must assume a role (with MFA required) to access S3 buckets in the same AWS account. Create a configuration for AWS CLI that is supported in Cyberduck and Mountain Duck using the S3 (Credentials from AWS Command Line Interface) connection profile or use the S3 (STS Assume Role) connection profile with no additional configuration.
Note
No custom configuration required with AWS S3 (STS Assume Role) connection profile available from Preferences… → Profiles.
Create a bookmark in Cyberduck or Mountain Duck
Open Preferences… → Profiles in Cyberduck or Mountain Duck.
Enable the AWS S3 (STS Assume Role) connection profile.
Add a new Bookmark in Cyberduck or Mountain Duck and choose AWS S3 (STS Assume Role) connection profile in the protocol dropdown.
Create a user with both access keys and a MFA device configured
In AWS IAM console create a new user. Do not grant this user any permissions for S3.
In the Security credentials tab, choose Create access key and copy to the clipboard.
Enter access key ID and secret access key in the bookmark.
Assign a MFA device to the user in Multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Tip
To allow entering the code in Cyberduck or Mountain Duck when connecting, make sure to choose Authenticator app or Hardware TOTP token as a MFA device. Using Passkey MFA does not allow getting a numeric MFA code.
Copy the MFA device ARN to the clipboard.
Create IAM role allowing access to S3 enforcing the MFA requirement
In AWS IAM console create a new IAM role that has S3 permissions and requires MFA. The IAM role must have the trusted entity set to the previously created user’s ARN.
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::<ACCOUNT_ID>:user/<S3_USER>" }, "Action": "sts:AssumeRole", "Condition": { "Bool": { "aws:MultiFactorAuthPresent": "true" } } } ] }
Copy the Role ARN to the clipboard.
Attach a permission policy to the role that grants access to S3 such as the managed policy
AmazonS3FullAccess.{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:*" ], "Resource": "*" } ] }
Restrict the permissions as necessary.
Add inline policy to allow the user to assume the role with sts:AssumeRole
Navigate to the previously added IAM user to attach the
sts:AssumeRolepermission as an inline policy.Add a permission policy for the user by choosing Add permissions → Create inline policy in the Permissions tab. In the policy editor opened, add the action
sts:AssumeRolefor the resource ARN referencing the IAM role<S3-ROLE-NAME>created previously allowing access to S3 with MFA.{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "sts:AssumeRole", "Resource": "arn:aws:iam::<Account ID>:role/S3-ROLE-NAME" } ] }
Connect to S3 using the bookmark
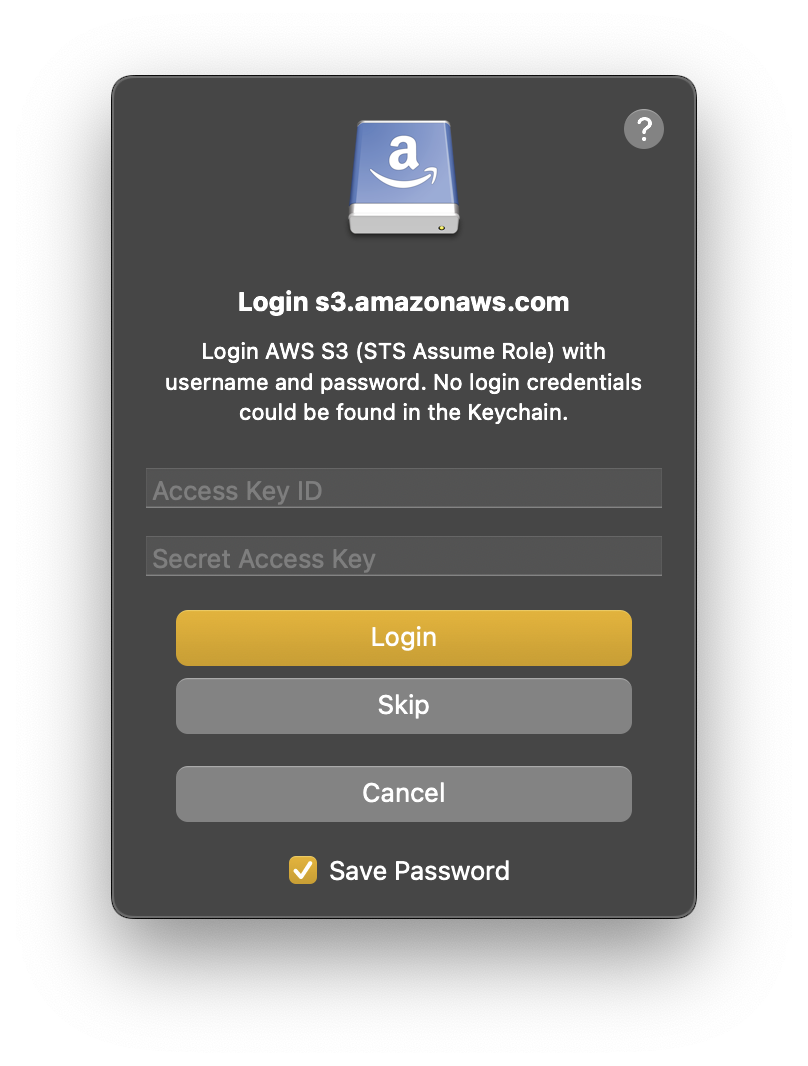
When not already configured in the bookmark, enter the static AWS credentials for the user with the permission to assume the IAM role when prompted.
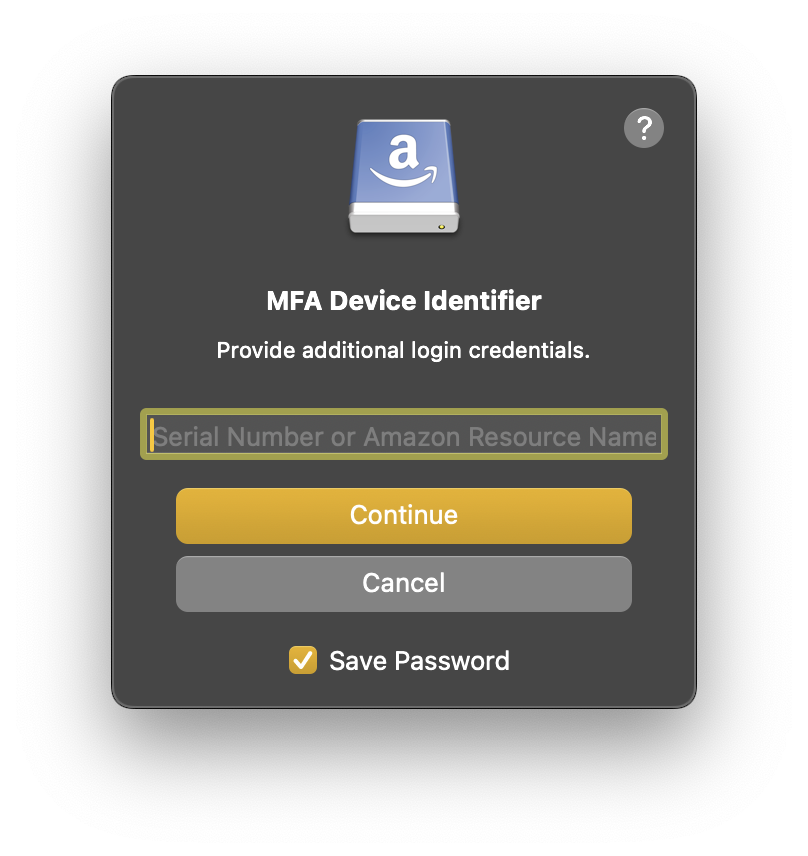
Enter the MFA device identification when prompted.
Tip
Enter the identification number of the MFA device that is associated with the user. The value is either the serial number for a hardware device (such as
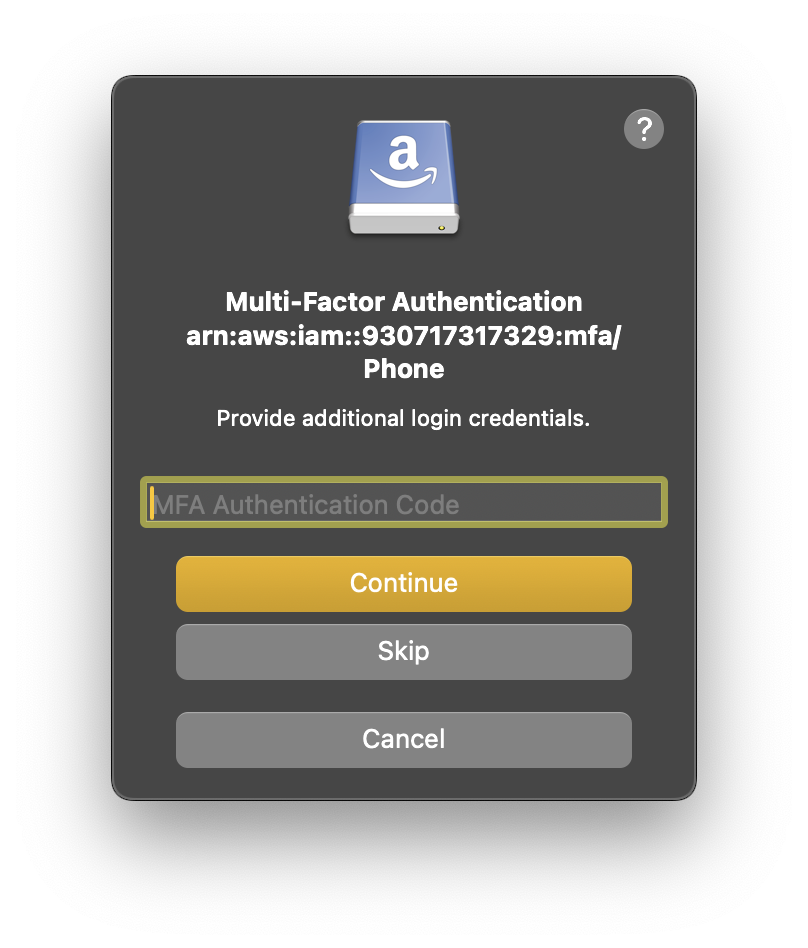
<code>GAHT12345678</code>) or an Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for a virtual device (such as<code>arn:aws:iam::123456789012:mfa/device</code>)Enter the one-time MFA code from your device when prompted.
Troubleshooting
User: arn:aws:iam::<ACCOUNT_ID>:user/<USERNAME> is not authorized to perform: s3:ListAllMyBuckets because no identity-based policy allows the s3:ListAllMyBuckets action.
This error occurs when the user does not have permission to list all buckets in the account. Possibly no attempt to assume the role was made.
The security token included in the request is invalid.
The AWS access key ID and secret access key set for the bookmark are invalid.
MultiFactorAuthentication failed with invalid MFA one time pass code.
The one-time MFA code already expired or is invalid.
Alternative: Using AWS CLI Configuration
Alternatively use the S3 (Credentials from AWS Command Line Interface) profile to read values from the AWS CLI ~/aws/credentials file.
Copy the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key to a profile in
~/.aws/credentials[<S3_USER>] aws_access_key_id=AKIA… aws_secret_access_key=…
Copy the MFA ARN and reference it in the
mfa_serialparameter in the<S3-ROLE-NAME>profile in~/.aws/credentials. This will require the user to enter a MFA code when assuming a role with a S3 access policy attached when connecting.[<S3-ROLE-NAME>] source_profile=<S3_USER> role_arn=arn:aws:iam::<Account ID>:role/<S3-ROLE-NAME> mfa_serial=arn:aws:iam::<Account ID>:mfa/<MFA-DEVICE-NAME>
Enter the alias
<S3-ROLE-NAME>for the role configuration from your AWS CLI configuration in Server of the bookmark.
Alternative: Use Custom Connection Profile
Add the
role_arnandmfa_serialto a custom connection profile to skip the prompts on connect.<key>Role Configurable</key> <true/> <key>Multi Factor Configurable</key> <true/> <key>Properties</key> <dict> <!-- Can be left blank to require Role ARN input from user --> <key>role_arn</key> <string>arn:aws:iam::<Account ID>:role/<S3-ROLE-NAME></string> <!-- Can be left blank to require MFA ARN input from user when assuming role requires token from MFA --> <key>mfa_serial</key> <string>arn:aws:iam::<Account ID>:mfa/<MFA-DEVICE-NAME></string> </dict>